Smart Grids: Opportunities and Challenges
Dr. Mustapha Taoumi
Clean Energy Technology Expert
EU – Clean Energy Technology Network
Email: m.taoumi@gmail.com

|
The basic structure of the electric power grid has remained unchanged for more than hundred years. Indeed, the existing power generation infrastructure is not able to keep pace with growing power demand. Also, the methods of power delivery to consumers are also outdated and extremely inefficient. Smart grids will enable new sources of energy (mainly Renewables Energy) and new forms of demand. They can help us keep the lights on at minimum cost to consumers, while creating jobs and enhancing economic growth. They can support our low carbon transition and create opportunities for consumers to play an active role in the energy system alongside generators, suppliers and network companies. |
On the other hand, the electric grid in its current state is falling behind the 21st century technological advancements and energy demands while the current trends in energy supply and use are unsustainable-economically, environmentally and socially. To ensure dependable and sustainable supply of electricity, a modern power grid is necessary which will be smarter. This new technology ensures effective control of electric supply and demand using information technology, and assures the potential use of eco-friendly power generation. Furthermore, implementation of Smart Grids concepts and infrastructure can be a better tool to develop greener and digital power. |
Smart Grids: Approaches
|
Around the world different approaches are being adopted and a wide variety of technologies and services are being demonstrated driven by national and regional business drivers. 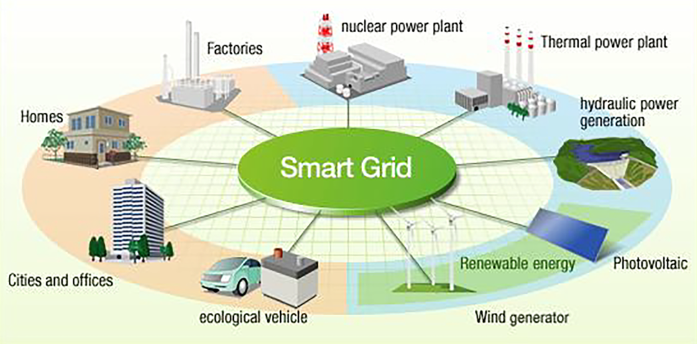
Basically, Smart Grid as a new infrastructure for supplying power will leverage ICT technology to improve the reliability of power supplies, promote the mass introduction of renewable energy and optimize energy use by consumers. Based on a power supply network which is responsible for supplying power, and a communication network which supervises and controls the facilities that constitute the power supply network, ICT technology will allow power consumers to upgrade their energy management across power generations. Overall, Smart Grids will enable high-quality power to be supplied in a highly efficient manner and thus promote a rich, safe and low carbon society. |
Advantages
For Power Companies:
For End Users:
|
Smart Meters and Smart Appliances
|
While the smart grid components comprises the ability to integrate renewables and storage systems as well as integrated communication systems, the current system of energy metering as well as billing still uses electromechanical and somewhere digital meter whichconsumes more time and labour. Billing inaccuracy is also considered as an issue for many consumers, which increase the number of complaints that the utility/distribution company have to overcome. By introducing smart meters and smart appliances the following issues would be addressed:
|

|
|
Smart Grids: Challenges Despite the benefits of smart grids, some challenges remains as barriers to their implementation such:
|
References
|